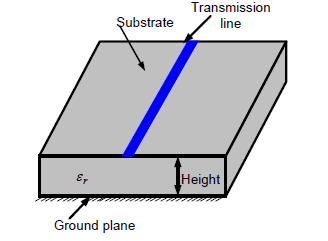
Microwave filters
Introduction
A filter is a two-port network used to control the frequency
response at a certain pointin an RF or microwave system by providing
transmission at frequencies within the passbandof the filter and attenuation in
the stopband of the filter.
Microwave
filters represent a class of electronic filter design to operate on signals in
the MHz to GHz frequency ranges. This frequency range is the range used by most
broadcast radio, television, wireless communications like Cell phone, Wi-Fi,
Wi-Max and the most radio frequency and microwave devices will include some
kinds of filtering on the signals transmitted or received.